Consumer price inflation in Pakistan jumped to a record 35.37 per cent in March from a year earlier, the statistics bureau said on Saturday, as at least 16 people were killed in stampedes for food aid.
The March inflation number eclipsed February's 31.5 per cent, the bureau said, as food, beverage, and transport prices surged up to 50 per cent year-on-year.
Thousands of people have gathered at flour distribution centres set up across the country, some as part of a government-backed programme to ease the impact of inflation.
At least 16 people, including five women and three children, have been killed in stampedes at such centres in recent days, police and officials have said. According to official records, thousands of flour bags have also been looted from trucks and distribution points.
A spokesman at the statistics bureau said the inflation number was the highest ever year-on-year increase recorded by the bureau since monthly records began in the 1970s.
"This is the highest ever inflation recorded in the data we have," he said.
The bureau said the consumer price index was up 3.72 per cent in March from the previous month.
Higher prices of food, cooking oil and electricity pushed up the index, it said.
Annual food inflation in March was at 47.1 per cent and 50.2 per cent for urban and rural areas, respectively, the bureau said. Core inflation, which strips out food and energy, stood at 18.6 per cent in urban areas and 23.1% per cent in rural areas.
The South Asian nation has been in economic turmoil for months with an acute balance of payments crisis while talks with the IMF to secure $1.1 billion (AED 4 billion) in funding as part of the $6.5 billion (AED 22 billion)bailout agreed in 2019 have not yet yielded fruit.
Pakistan's foreign exchange reserves have fallen to cover barely four weeks of imports.
A monthly economic outlook report issued by the finance ministry on Friday projected inflation would remain elevated.
The report cited market frictions caused by relative demand and supply gaps of essential items, exchange rate depreciation, and the recent upward adjustment in fuel prices as reasons behind higher inflation expectations.
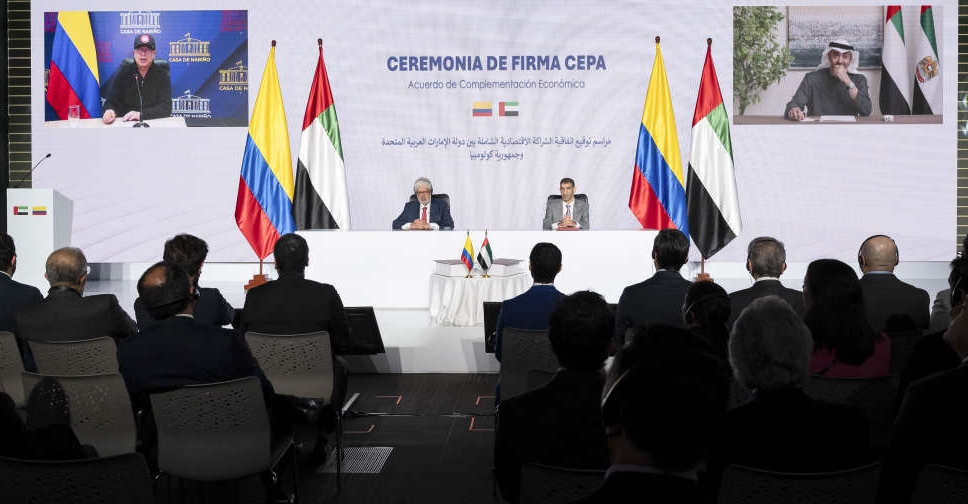
 UAE, Colombia sign major trade pact
UAE, Colombia sign major trade pact
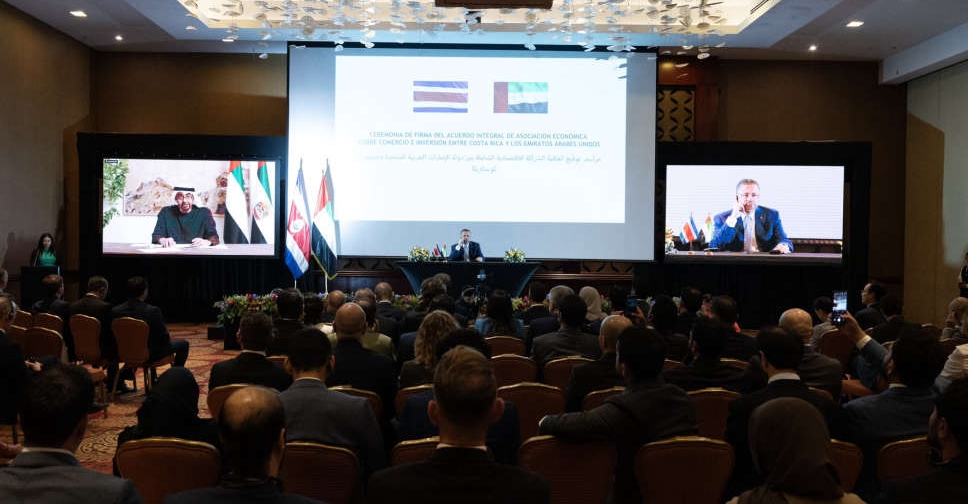 UAE and Costa Rica sign economic partnership deal
UAE and Costa Rica sign economic partnership deal
 Dubai-based Telegram app to hit 1 billion users 'within a year'
Dubai-based Telegram app to hit 1 billion users 'within a year'
 Microsoft invests $1.5 billion in Abu Dhabi AI company G42
Microsoft invests $1.5 billion in Abu Dhabi AI company G42
 Spinneys announces intention to float on Dubai Financial Market
Spinneys announces intention to float on Dubai Financial Market




